Quiz Ancient history
Last Updated:
Fascinated by ancient history? Our quizzes on this captivating period are made for you! Test your knowledge of the great civilizations, iconic figures, famous battles and monuments that marked the ancient history.
Our ancient history quizzes are a fun and rewarding way to delve into the world of the Greeks, Romans, Egyptians and many other fascinating cultures. With a varied selection of questions, you can test your knowledge on subjects such as Greek mythology, the pharaohs, the conquests of Alexander the Great and the technical achievements of the Romans.
Do you know where Babylon was? Can you name the seven wonders of the ancient world? Do you know the great philosophers Socrates, Aristotle and Plato? Our ancient history quizzes will help you answer all these questions, while enriching your knowledge of this fascinating era.
As you explore our ancient history quizzes, you’ll discover fascinating anecdotes, striking facts and surprising details about the societies that laid the foundations of our civilization. Whether you’re a history buff, a student or simply curious, our quizzes are an interactive and entertaining way to test your knowledge and learn more about ancient history.
Test your knowledge now and embark on a journey back in time to the era of the great ancient civilizations!
Test your knowledge of Ancient history with our quizzes. Whether you’re an amateur or an expert in history, our quizzes will provide you with a challenge adapted to your level.
Compare yourself with other history buffs and find out where you stand among connoisseurs of the great ancient civilizations. Each question is an opportunity to learn and deepen your knowledge.
Our Ancient history quizzes are not simple knowledge tests, but interactive learning tools. Each question is accompanied by detailed explanations and interesting facts about ancient events, people, monuments and cultures.
By answering the questions, you’ll enrich your general knowledge and develop a better understanding of this key period in history. Use our quizzes to explore ancient civilizations, discover fascinating anecdotes and strengthen your ancient history skills.
history
/ 10
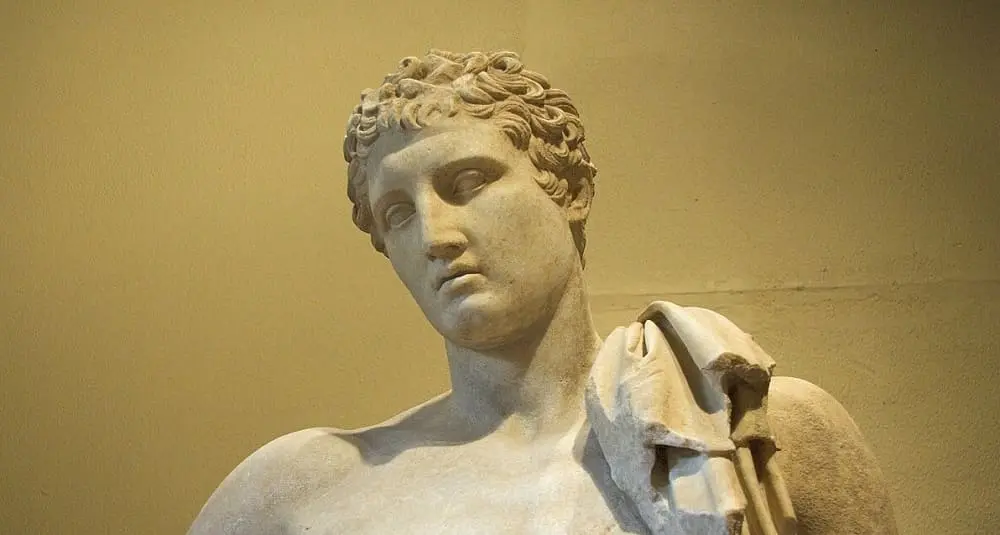

Who is Hermes in mythology?
2Messenger of the gods
1God of war

🙌 Good answer
In Greek mythology, Hermes is the messenger of the gods, the god of trade, travel, thieves and eloquence. He also guides souls to the Underworld.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
In Greek mythology, Hermes is the messenger of the gods, the god of trade, travel, thieves and eloquence. He also guides souls to the Underworld.
Next question
history
/ 10
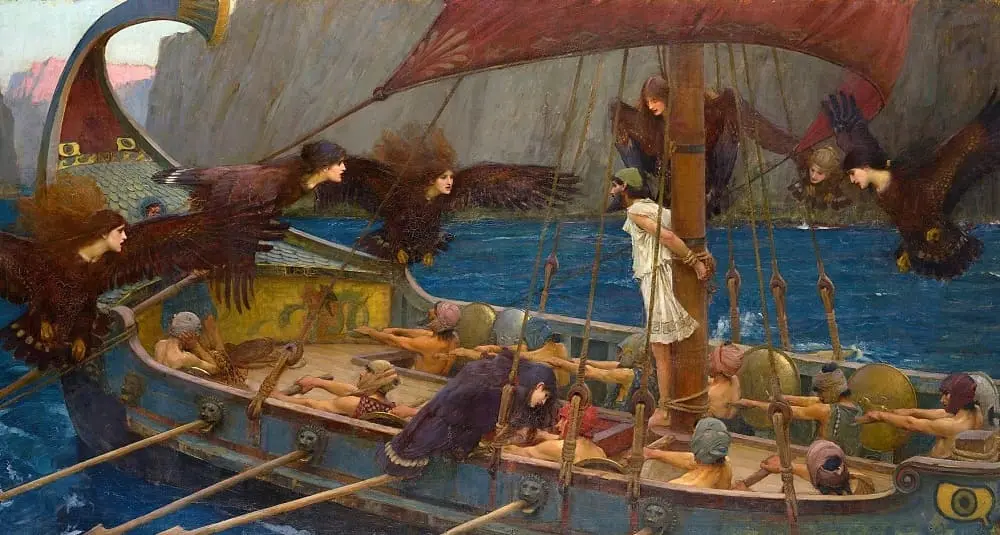

How long is Ulysses' journey?
220 years
110 years

🙌 Good answer
Ulysses' voyage lasts 20 years: 10 years for the Trojan War and 10 years of wandering before his return to Ithaca, as recounted in Homer's Odyssey.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Ulysses' voyage lasts 20 years: 10 years for the Trojan War and 10 years of wandering before his return to Ithaca, as recounted in Homer's Odyssey.
Next question
history
/ 10

What does Janus symbolize?
1Past and future
2War and peace

🙌 Good answer
In Roman mythology, Janus symbolizes beginnings, endings, the passage of time and transitions, with his two faces turned towards the past and the future.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
In Roman mythology, Janus symbolizes beginnings, endings, the passage of time and transitions, with his two faces turned towards the past and the future.
Next question
history
/ 10
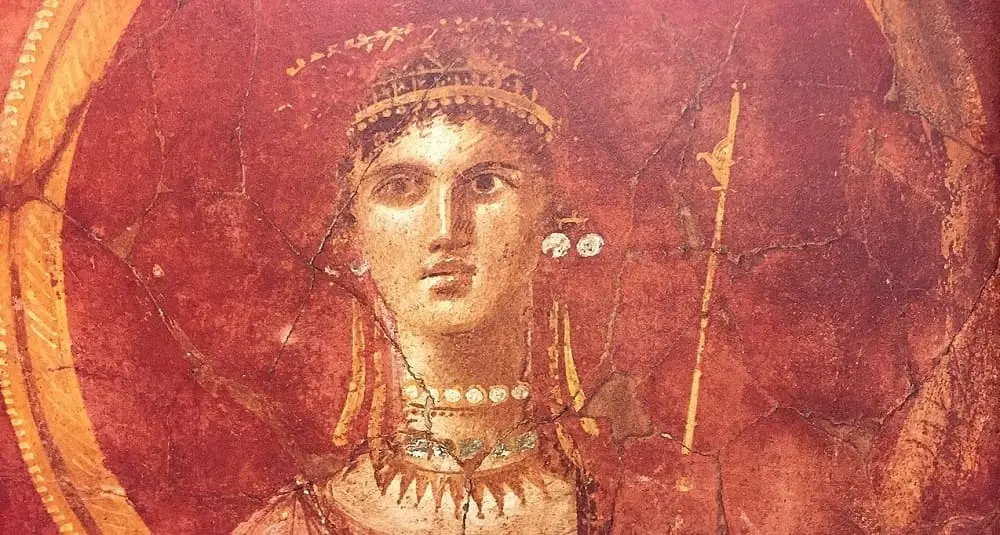

Who is Aphrodite?
1Goddess of love
2Goddess of wisdom

🙌 Good answer
In Greek mythology, Aphrodite is the goddess of love, beauty and desire. Born of sea foam, she is one of the most influential Olympian deities.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
In Greek mythology, Aphrodite is the goddess of love, beauty and desire. Born of sea foam, she is one of the most influential Olympian deities.
Next question
history
/ 10
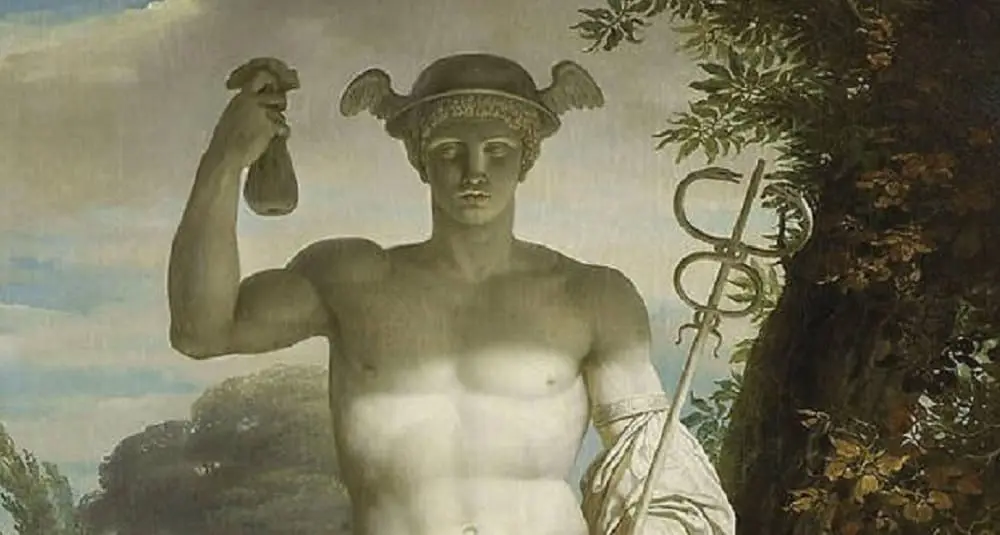

What is Mercury's Greek name?
2Hermes
1Ares

🙌 Good answer
Mercury's Greek name is Hermes. In Greek mythology, he is the messenger of the gods, protector of travelers, merchants and thieves.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Mercury's Greek name is Hermes. In Greek mythology, he is the messenger of the gods, protector of travelers, merchants and thieves.
Next question
history
/ 10
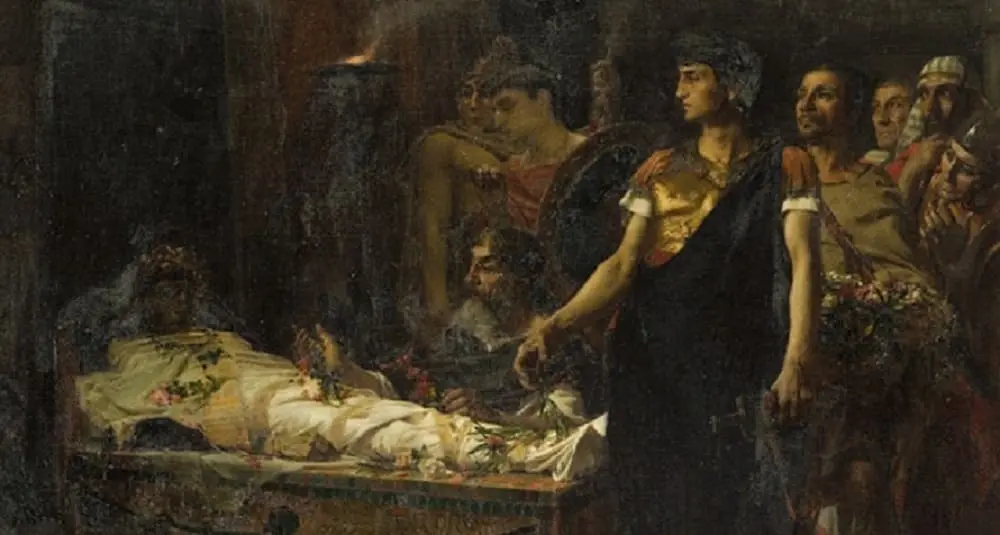

How did Alexander the Great die?
2Sudden fever
1Murder

🙌 Good answer
Alexander the Great died in Babylon in 323 BC, probably as a result of a febrile illness.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Alexander the Great died in Babylon in 323 BC, probably as a result of a febrile illness.
Next question
history
/ 10
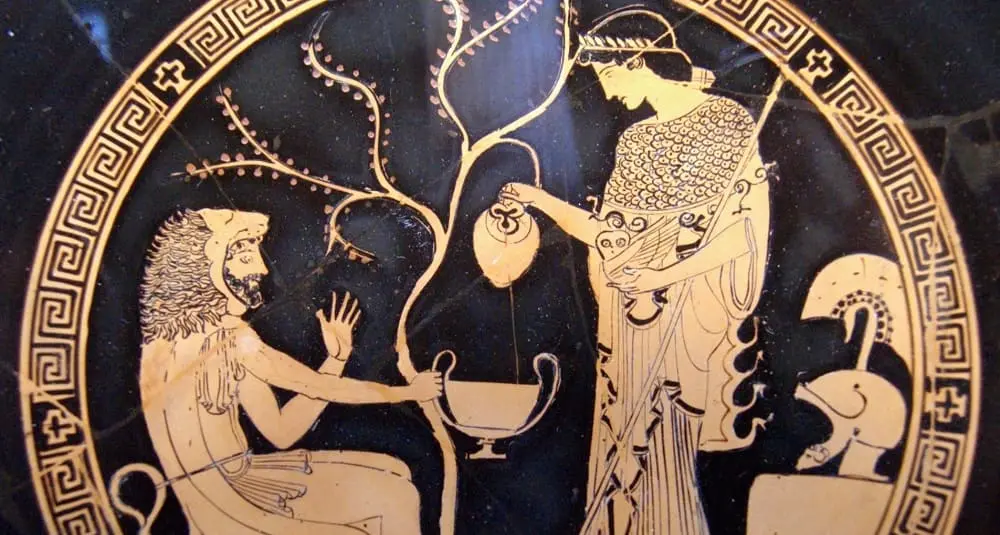

Which animal is often associated with the Greek goddess Athena?
1Owl
2Snake

🙌 Good answer
In Greek mythology, the animal associated with Athena is the owl. A symbol of wisdom and knowledge, it embodies intelligence and clairvoyance.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
In Greek mythology, the animal associated with Athena is the owl. A symbol of wisdom and knowledge, it embodies intelligence and clairvoyance.
Next question
history
/ 10
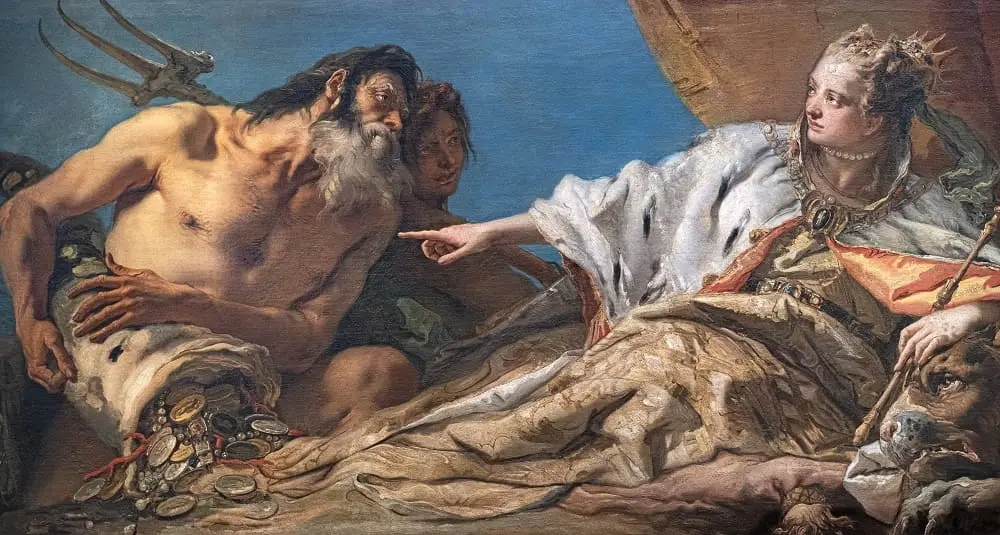

Who is the Roman god of the sea?
1Neptune
2Poseidon

🙌 Good answer
In Roman mythology, Neptune is the god of the sea. He reigns over oceans, storms and horses, the equivalent of the Greek god Poseidon.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
In Roman mythology, Neptune is the god of the sea. He reigns over oceans, storms and horses, the equivalent of the Greek god Poseidon.
Next question
history
/ 10
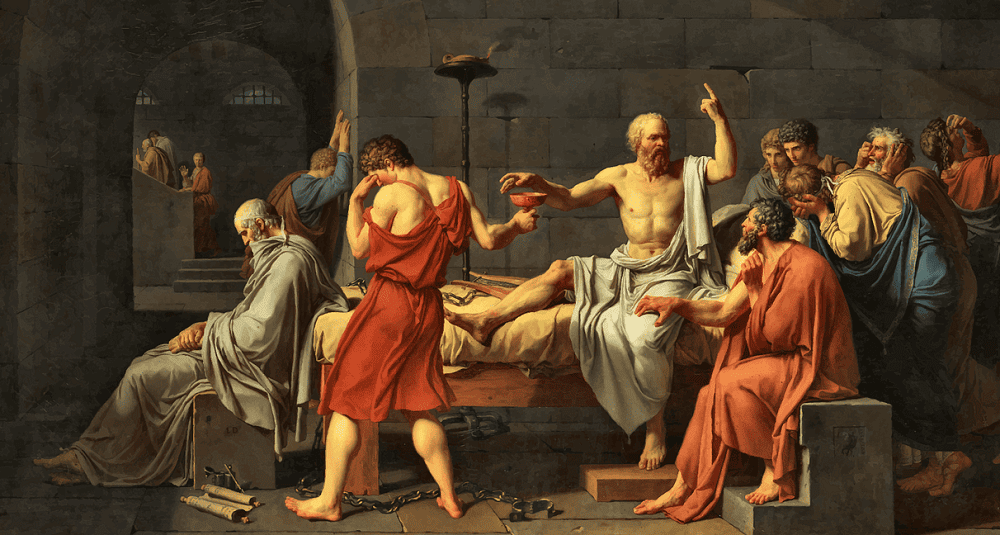

How did Socrates die?
2Forced suicide
1Died in battle

🙌 Good answer
Socrates died in 399 BC after drinking the deadly poison hemlock. Condemned by Athens for impiety and corruption of youth, he accepted his fate.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Socrates died in 399 BC after drinking the deadly poison hemlock. Condemned by Athens for impiety and corruption of youth, he accepted his fate.
Next question
history
/ 10
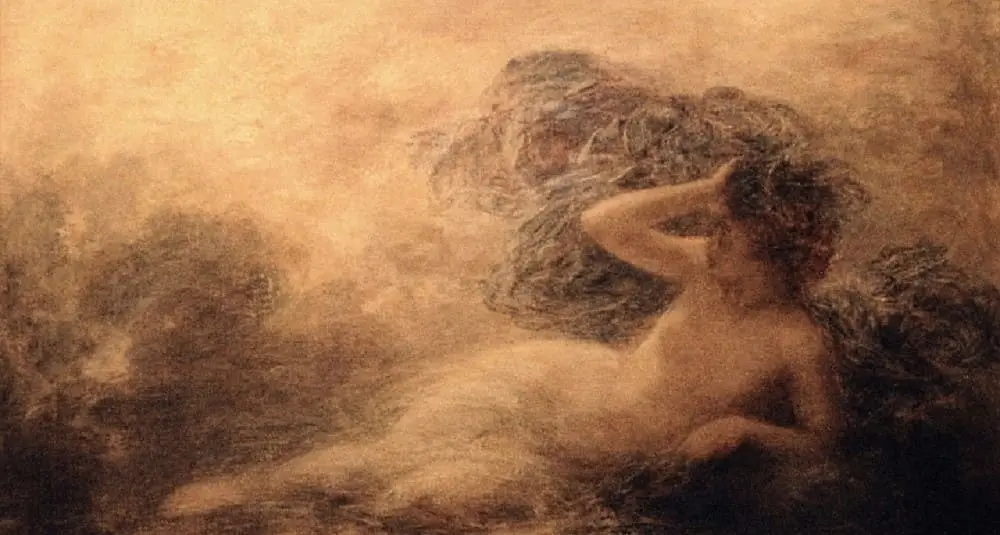

Who is the goddess Nyx?
2Goddess of the night
1Goddess of Dawn

🙌 Good answer
In Greek mythology, Nyx is the primordial goddess of the night, mother of Hypnos (sleep) and Thanatos (death), feared even by Zeus.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
In Greek mythology, Nyx is the primordial goddess of the night, mother of Hypnos (sleep) and Thanatos (death), feared even by Zeus.
Next question