When were the paleolithic paintings and engravings in the Chauvet Cave discovered?
Last Updated:
The Paleolithic paintings and engravings in the Chauvet cave were discovered in 1994. The discovery was made by a group of cavers led by Jean-Marie Chauvet, Éliette Brunel-Deschamps and Christian Hillaire in southern France, near Vallon-Pont-d’Arc, in the Ardèche region.
The Chauvet cave quickly became famous for the quality, diversity and age of its rock art. The paintings and engravings date back over 30,000 years, making it one of the oldest known prehistoric art sites in the world. The works depict a wide variety of animals, including lions, mammoths, rhinoceroses and horses, and demonstrate a high level of artistic skill and sophistication.
Because of its exceptional value, the Chauvet cave was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2014. To protect these precious works, the cave itself is closed to the public, but an exact replica, the Caverne du Pont-d’Arc, was opened in 2015 to allow the public to discover and appreciate this incredible heritage without damaging the original.
The discovery of the Chauvet cave has profoundly enriched our understanding of prehistoric art and early human life in Europe. It remains an important subject of study for archaeologists, prehistorians and rock art enthusiasts alike.
The Paleolithic paintings and engravings in the Chauvet cave were discovered in 1994. This exceptional site, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is one of the world’s most important examples of prehistoric art, illustrating the talent and creativity of early man.
history
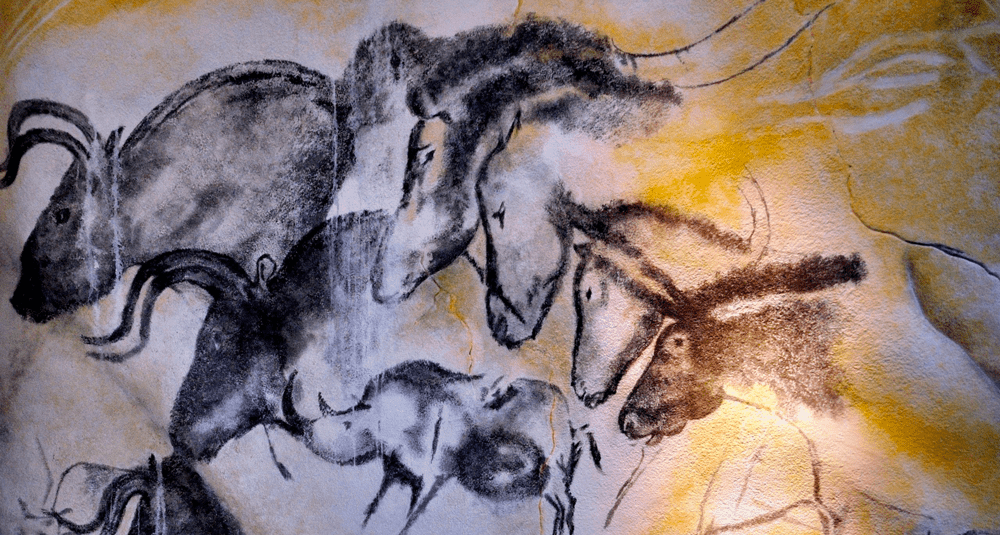
When were the paleolithic paintings and engravings in the Chauvet Cave discovered?
Answer
The Paleolithic paintings and engravings at Chauvet cave were discovered in 1994. This prehistoric site is one of the most important in the world for rock art.