Which space probe was launched in 2018 to study the solar corona?
Last Updated:
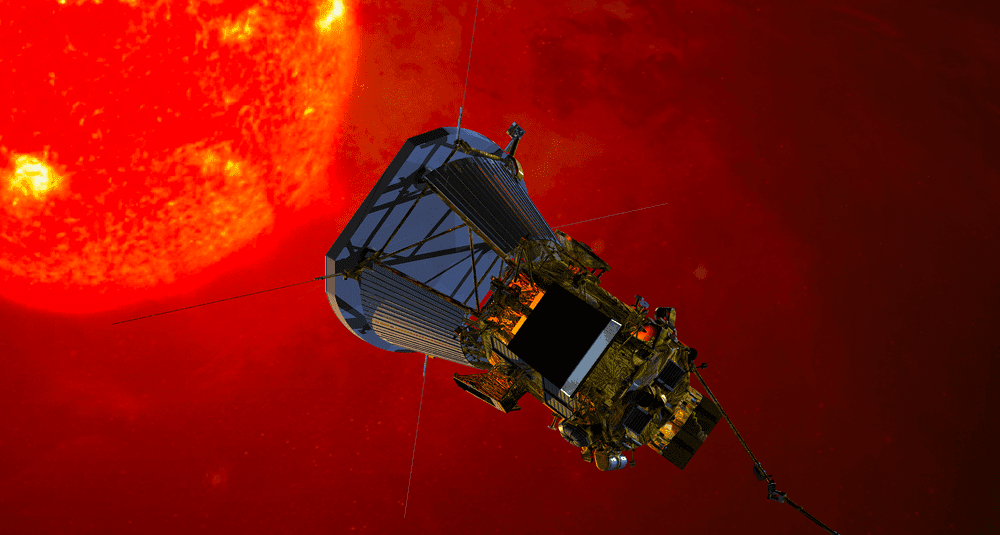
The Parker probe, officially known as the Parker Solar Probe, is a space probe launched by NASA in 2018 whose main mission is to study the solar corona, the mysterious outer layer of the Sun’s atmosphere. This mission is one of the most ambitious projects in contemporary space exploration, as never before has a probe come so close to our star for such a long period of time.
The Parker probe was launched on August 12, 2018, from Cape Canaveral, Florida, aboard a Delta IV Heavy rocket. This is NASA’s first mission to be named after a living scientist, Eugene Parker, an American astrophysicist who theorized the existence of solar wind in the 1950s. This tribute highlights the historical importance of his work and the continuity between theoretical research and practical exploration.
The main objective of the mission is to solve several fundamental mysteries about the Sun. The solar corona has long intrigued researchers because it has a surprising characteristic: its temperature is much higher than that of the solar surface (the photosphere). While the surface reaches about 5,500°C, the corona can exceed several million degrees. Understanding this paradox is one of the great challenges that the Parker probe is striving to address.
To accomplish this mission, the probe was designed to fly extremely close to the Sun, approximately 6.16 million kilometers from its surface, seven times closer than any previous probe. At this distance, Parker’s instruments must withstand extreme conditions, including temperatures exceeding 1,300°C and intense radiation. To protect itself, the spacecraft is equipped with a revolutionary 11.5 cm-thick carbon composite heat shield capable of keeping the scientific instruments at a temperature of around 30°C despite the scorching environment.
The Parker spacecraft carries several instruments designed to measure solar wind, magnetic fields, and energetic particles. This data is crucial not only for a fundamental understanding of the Sun, but also for practical applications. Solar wind and solar flares can have a direct impact on Earth, disrupting communications, satellites, and even power grids. A better understanding of these phenomena makes it possible to better anticipate “solar storms” and strengthen the protection of human infrastructure.
The mission is expected to last until 2025, during which time the probe will complete 24 orbits around the Sun. Thanks to gravitational assistance from the planet Venus, Parker gets a little closer to our star with each pass. The initial data collected since its launch has already led to major advances, including the discovery of unexpected magnetic structures in the solar wind, known as “switchbacks,” and a better understanding of the origin and acceleration of this wind.
The Parker probe is therefore not only a technological feat, it represents a leap forward for humanity in its quest to understand the fundamental mechanisms of the star that makes life possible on Earth. It also helps to strengthen our ability to predict solar activity and protect our increasingly technology-dependent civilization.
Launched by NASA in 2018, the Parker Solar Probe is dedicated to studying the solar corona. Its mission aims to solve age-old mysteries about the Sun’s temperature and behavior, while improving our ability to predict solar phenomena. This is a historic step in space exploration and a demonstration of human ingenuity in the service of science.
sciences
Which space probe was launched in 2018 to study the solar corona?
Answer
The Parker Solar Probe, launched in 2018 by NASA, has the mission of studying the solar corona and unraveling the mysteries of the Sun's atmosphere.