Against which infectious disease is the Calmette and Guérin bivalent vaccine used?
Last Updated:
The BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) vaccine is used to prevent tuberculosis, an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Developed by French researchers Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin, the vaccine was first introduced in 1921. Tuberculosis is a serious disease that mainly affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine and brain.
Tuberculosis is transmitted by air, when people with pulmonary tuberculosis cough, sneeze or talk, dispersing droplets containing bacteria into the air. Although tuberculosis can be treated and cured, it remains one of the world’s leading causes of death, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
The BCG vaccine is particularly recommended for infants and young children in countries where tuberculosis is common. It is not commonly administered in countries where tuberculosis is rare, such as the United States, due to its low efficacy in adults and the relatively low incidence of the disease.
The BCG vaccine plays a crucial role in the fight against tuberculosis, offering essential protection against this dangerous infectious disease.
sciences
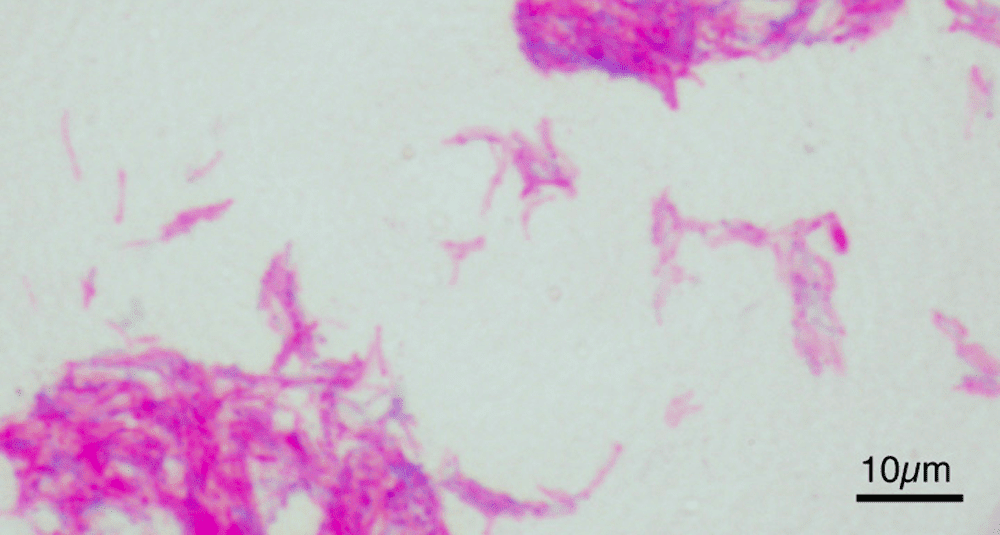
Against which infectious disease is the Calmette and Guérin bivalent vaccine used?
Answer
The BCG (Calmette-Guérin) vaccine is used to prevent tuberculosis, an infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs.