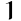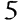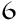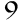Quiz History
Last Updated:
Are you a history buff? Our quizzes are for you! Test your knowledge of the great historical periods, landmark events, famous people and civilizations that have shaped the world as we know it today.
Our history quizzes are a fun and educational way to relive key moments in human history. With a varied selection of questions, you can test your knowledge on topics ranging from antiquity to the 21st century, including the Middle Ages, the Renaissance, industrial and political revolutions.
Do you know who signed the U.S. Declaration of Independence? Do you know the dates of major battles such as Hastings and Waterloo? Can you identify iconic figures such as Napoleon, Cleopatra and Martin Luther King? Our history quizzes are designed to help you answer all these questions while enriching your historical knowledge.
As you explore our history quizzes, you’ll discover fascinating anecdotes, little-known facts and striking details about the events and characters that changed the course of history. Whether you’re a history buff, a student or simply curious, our quizzes are an interactive and entertaining way to test your knowledge and learn more about the events that have shaped the world.
Test your knowledge and travel through the ages with our history quizzes!
Test your knowledge of history with our quizzes. Whether you’re an amateur or a true enthusiast, our quizzes will offer you a challenge adapted to your level.
Compare yourself with other history buffs and find out where you stand among connoisseurs of the great historical periods. Each question is an opportunity to learn and deepen your knowledge.
Our history quizzes are not simple knowledge tests, but interactive learning tools. Each question is accompanied by detailed explanations and interesting facts about key events, characters and eras.
By answering the questions, you’ll enrich your general knowledge and develop a better understanding of the past. Use our quizzes to explore new historical periods, discover fascinating anecdotes and strengthen your knowledge of world history.
history
/ 10

What famous battle led by Charles Martel took place in 732?
2Poitiers
1Avignon

🙌 Good answer
The famous battle fought by Charles Martel in 732 was the Battle of Poitiers. This decisive victory halted Muslim expansion in Western Europe.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
The famous battle fought by Charles Martel in 732 was the Battle of Poitiers. This decisive victory halted Muslim expansion in Western Europe.
Next question
history
/ 10

Which pope convoked the Council of Trent in 1542?
1Paul III
2Pie III

🙌 Good answer
The Council of Trent was convened in 1542 by Pope Paul III to respond to the Protestant Reformation and reaffirm Catholic doctrine.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
The Council of Trent was convened in 1542 by Pope Paul III to respond to the Protestant Reformation and reaffirm Catholic doctrine.
Next question
history
/ 10

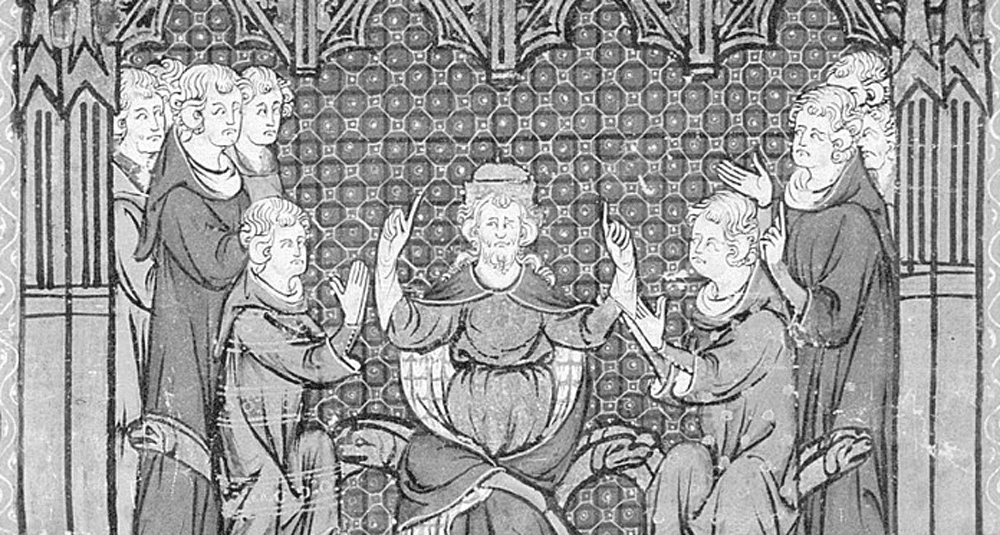
How did Emperor Marcus Aurelius die?
1Disease
2Murder

🙌 Good answer
Emperor Marcus Aurelius died in 180 AD, probably of the Antonine plague, during a military campaign near Vindobona, modern-day Vienna.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Emperor Marcus Aurelius died in 180 AD, probably of the Antonine plague, during a military campaign near Vindobona, modern-day Vienna.
Next question
history
/ 10

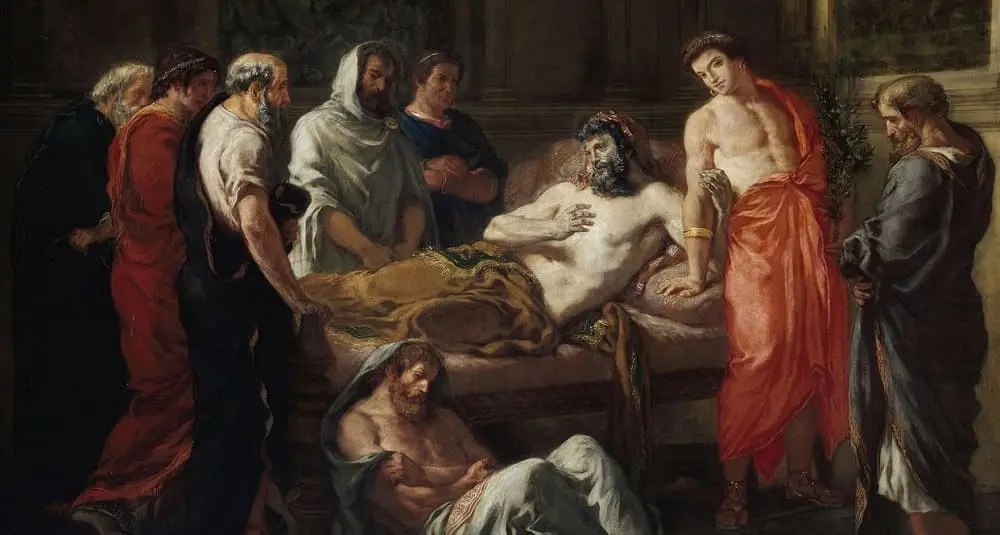
Which soldier is General-in-Chief of Confederate armies?
2Robert E. Lee
1Ulysses S. Grant

🙌 Good answer
Robert Lee is first the commander of the Virginia Armed Forces and then Chief General of the Confederate State Army.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Robert Lee is first the commander of the Virginia Armed Forces and then Chief General of the Confederate State Army.
Next question
history
/ 10
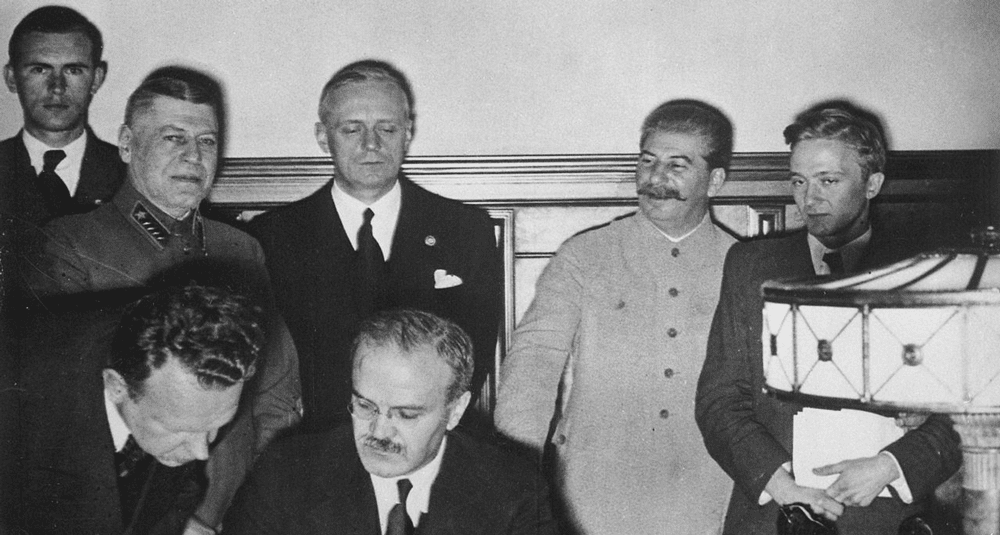

Where was the 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact signed?
2Moscow
1Berlin

🙌 Good answer
The German-Soviet Pact is a non-aggression treaty between Germany and the Soviet Union, signed in Moscow on August 23, 1939.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
The German-Soviet Pact is a non-aggression treaty between Germany and the Soviet Union, signed in Moscow on August 23, 1939.
Next question
history
/ 10
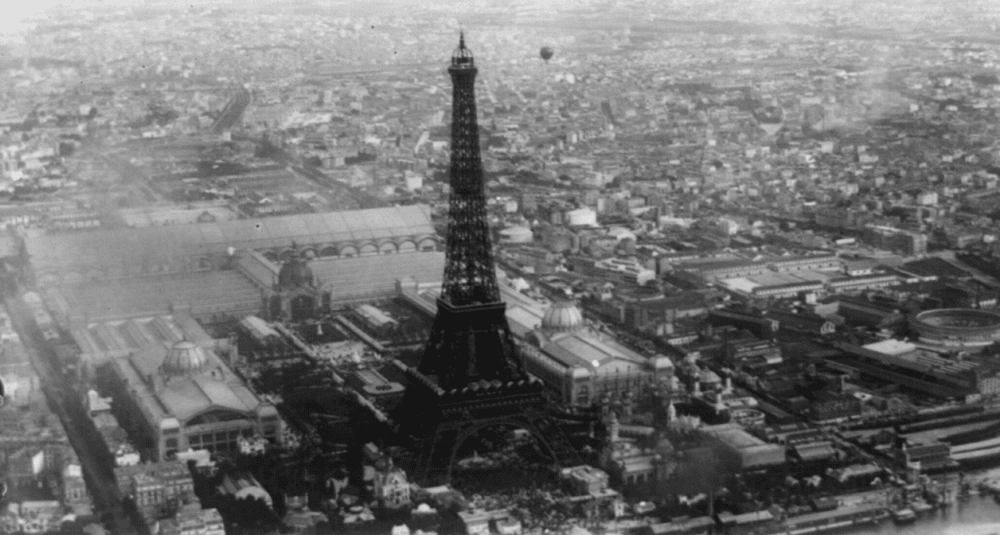
For which Universal Exhibition in Paris was the Eiffel Tower built?
1The Paris Universal Exhibition of 1889
2The Paris Universal Exhibition of 1900

🙌 Good answer
Built by Gustave Eiffel and his collaborators for the Universal Exhibition of Paris in 1889, and initially named "300-metre tower", this monument has become the symbol of the French capital and a major tourist site.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Built by Gustave Eiffel and his collaborators for the Universal Exhibition of Paris in 1889, and initially named "300-metre tower", this monument has become the symbol of the French capital and a major tourist site.
Next question
history
/ 10
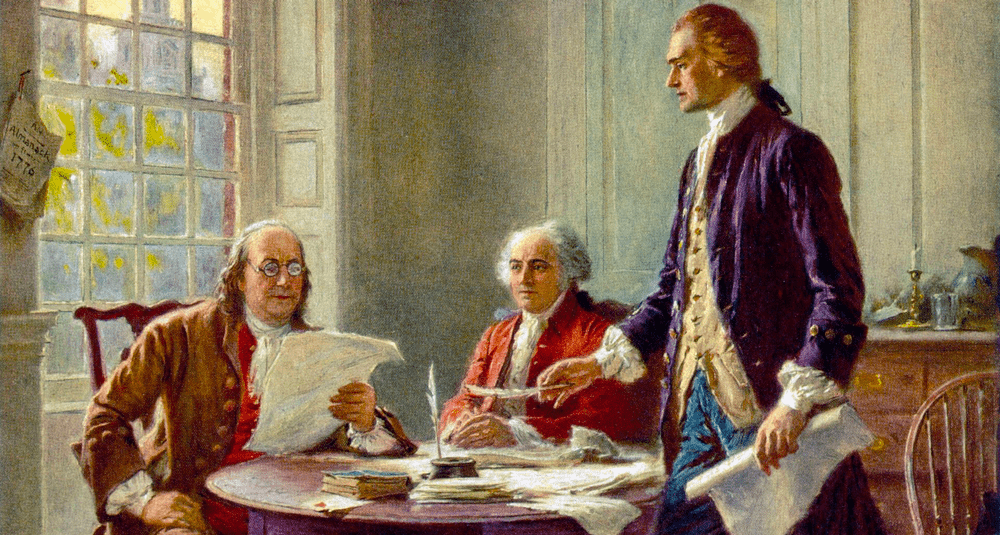
Who is the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence?
1Thomas Jefferson
2George Washington

🙌 Good answer
The project is assigned to a committee of five representatives (John Adams, Roger Sherman, Benjamin Franklin, Robert Livingston and Thomas Jefferson). Thomas Jefferson eventually developed a draft and became the principal author of the text.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
The project is assigned to a committee of five representatives (John Adams, Roger Sherman, Benjamin Franklin, Robert Livingston and Thomas Jefferson). Thomas Jefferson eventually developed a draft and became the principal author of the text.
Next question
history
/ 10
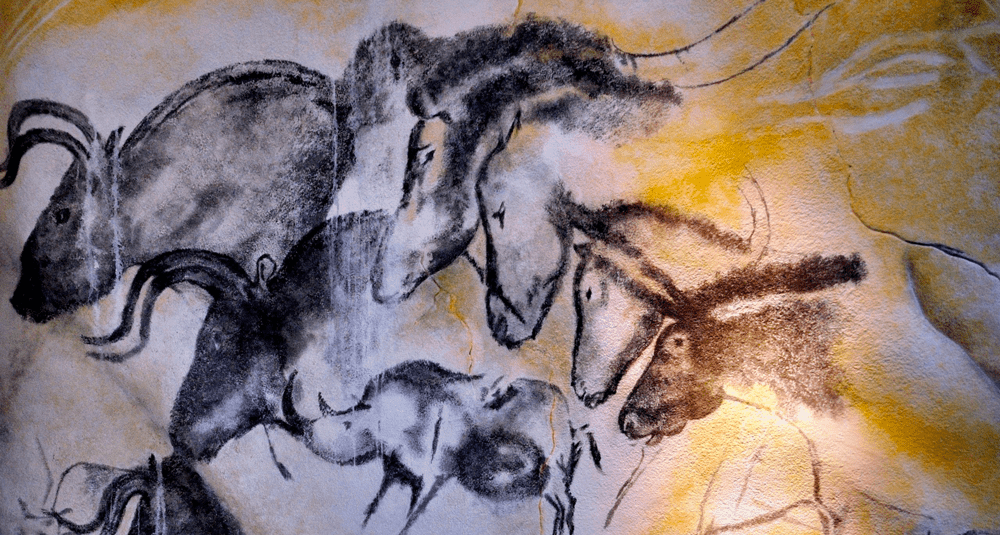
When were the paleolithic paintings and engravings in the Chauvet Cave discovered?
21994
11940

🙌 Good answer
The Paleolithic paintings and engravings at Chauvet cave were discovered in 1994. This prehistoric site is one of the most important in the world for rock art.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
The Paleolithic paintings and engravings at Chauvet cave were discovered in 1994. This prehistoric site is one of the most important in the world for rock art.
Next question
history
/ 10

When was slavery abolished in the United States?
21865
11863

🙌 Good answer
The abolition of slavery in the United States was officially proclaimed in 1865 with the adoption of the 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
The abolition of slavery in the United States was officially proclaimed in 1865 with the adoption of the 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
Next question
history
/ 10

To which branch of Christianity is Martin Luther the initiator?
2Protestantism
1Orthodoxie

🙌 Good answer
Martin Luther is the initiator of Protestantism which gave birth to many Protestant churches and marked the history of Christianity.
Next question

😞 Wrong answer
Martin Luther is the initiator of Protestantism which gave birth to many Protestant churches and marked the history of Christianity.
Next question