In which African biome can baobabs be found?
Last Updated:
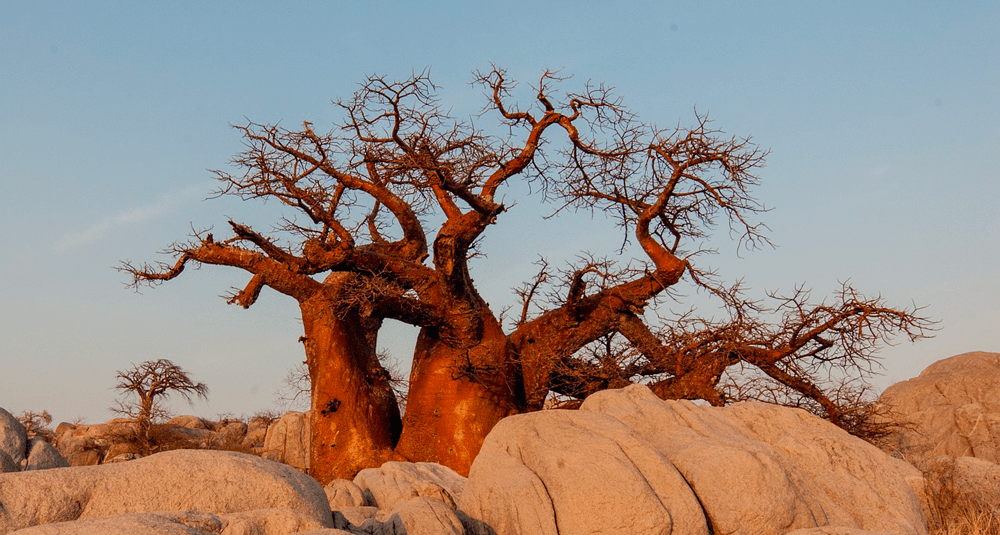
Baobabs are mainly found in African savannahs. The savannah is a biome characterized by vast expanses of grass dotted with scattered trees and bushes. Baobabs, which belong to the genus Adansonia, are particularly well adapted to the arid and semi-arid conditions of this biome, where rainfall is seasonal and sometimes unpredictable.
Baobabs are renowned for their massive trunks, which can store thousands of liters of water, enabling them to survive long periods of drought. Their bark is thick and tough, and their thick branches often extend in the shape of inverted roots, giving baobabs a unique and emblematic appearance.
There are several species of baobab in Africa, but the most widespread and emblematic is Adansonia digitata, often referred to simply as the African baobab. These trees are found mainly in sub-Saharan Africa, in countries such as Senegal, Mali, Zimbabwe, Namibia and Mozambique.
Baobabs play a crucial role in the savannah ecosystem. They provide food and shelter for many animals, such as elephants, who eat their bark and vitamin C-rich fruit. Man also uses baobabs for their leaves, seeds and edible fibers, which are used to make rope and other materials.
Baobabs are found mainly in the savannahs of Africa. These emblematic trees are well adapted to the arid and semi-arid conditions of this biome, where they play an essential role in the ecosystem and are used by animals and humans for a variety of resources.
You may also be interested in
nature
In which African biome can baobabs be found?
Answer
Baobabs are found mainly in the savannahs of Africa. These emblematic trees thrive in the continent's arid and semi-arid regions.